JETRO Invest Japan Report 2024
Chapter1. Global Trends in Inward FDI Section 3. Impact of Structural Changes in Global Value Chains (GVCs)
Unstable international situation changes GVC structure
In recent years, global companies have been required to strengthen and restructure their supply chains in a timely manner in order to deal with various international challenges and a competitive business environment that is necessary to use of the latest technologies, and this has led to changes in the structure of global value chains (GVCs). As a specific background, for instance, those are caused by the disruption of the existing economic structure due to the Covid-19 pandemic, the high demand for measures to deal with climate change, and the impact on procurement and distribution channels due to friction and disputes among nations.
JETRO has implemented a survey "Impact of Structural Changes in Global Value Chains (GVCs)" to reveal the responses of global companies to these highly volatile events and how they perceive the Japanese market. Based on the result of this survey, the factors that determine Foreign investment by global companies are considered in this section and in Section 6 of Chapter 2.
| Target companies |
|
|---|---|
| Target persons |
|
| Survey method |
|
| Period |
|
| Industry classification of respondents | Number of valid responses |
|---|---|
| Bio-Pharmaceutical | 6 |
| Storage battery | 5 |
| AI/Sensors, etc. (Industrial Robots/Automation) | 8 |
| Autonomous driving (Automobiles) | 4 |
| AI/Sensors and other ICT (Special vehicles) | 1 |
| Metaverse/Digital twin (industrial purpose) | 6 |
| Semiconductors | 6 |
| Biomaterial | 2 |
| Hydrogen fuel (Mobility) | 4 |
| Wind power (offshore) | 6 |
| Others | 14 |
| Total | 62 |
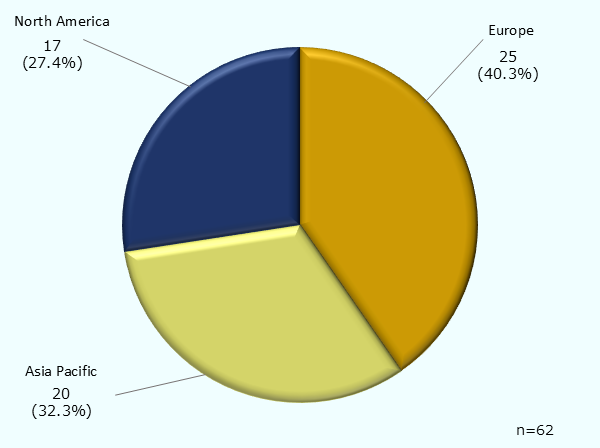
Note: The total does not necessarily equal 100% due to round off.
"Geopolitical conflicts and disputes" have a major impact on foreign investment strategies of global companies
The various events that lead to structural changes in GVCs can have a significant impact on the foreign investment strategies of global companies. In the survey, more than half (56.5%) of the respondent companies view "geopolitical conflicts and disputes" as one of the events that affect their business. Some companies mentioned the actual impacts, such as "business activities have been disrupted by the China-related supply chain problems and rising tensions in Southeast Asia," and "the war between Russia and Ukraine has forced us to close our offices in Russia."
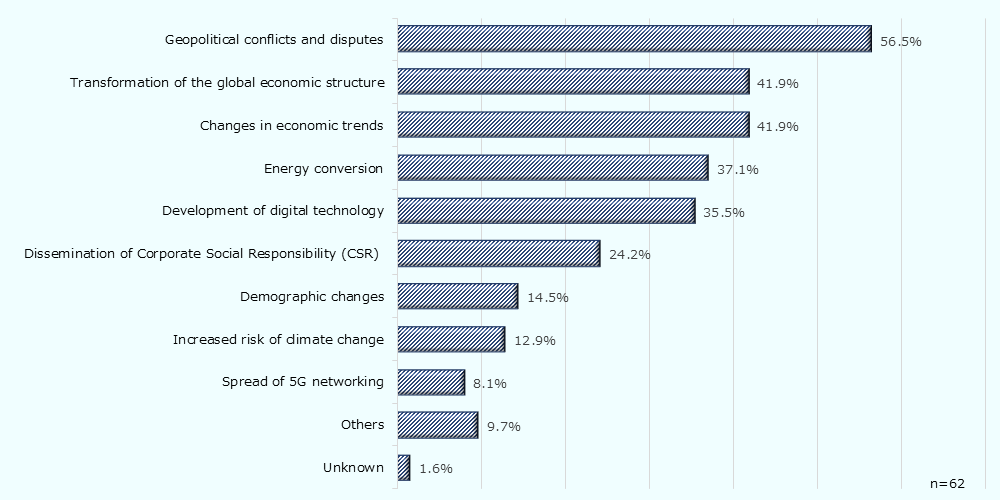
-
Note:
In the form of prioritizing up to three choices from among the choices.
Companies that selected at least one option were considered valid. -
Source:
JETRO's survey "Impact of Structural Changes in Global Value Chains (GVCs)"
Many companies have been affected in their China/Asia operations
Recent U.S.-China conflict, as an example, which is one of the Geopolitical conflicts, and it affects global companies’ operations in China/Asia. When asked whether the heightened geopolitical risk caused by the U.S.-China conflict is affecting their own businesses in China and other Asian countries, among the responded companies, about 67% of them in China and about 52% in Asia (other than China) answered "significant" or "to some extent." On the other hand, approximately 20% of the companies responded that they had had no impact.
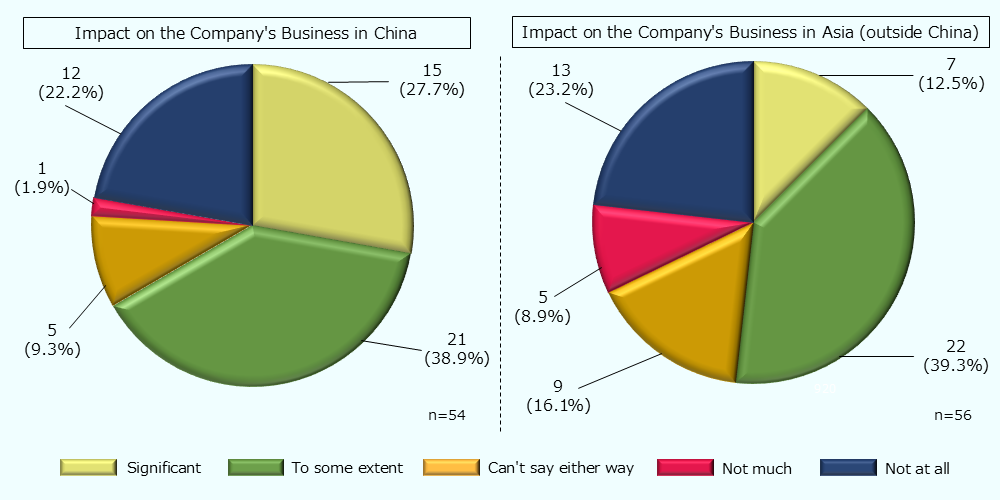
-
Note1:
The sum does not necessarily equal 100% due to rounding to one decimal place.
-
Note2:
Calculated excluding non-responses.
-
Source:
: JETRO's survey "Impact of Structural Changes in Global Value Chains (GVCs)"
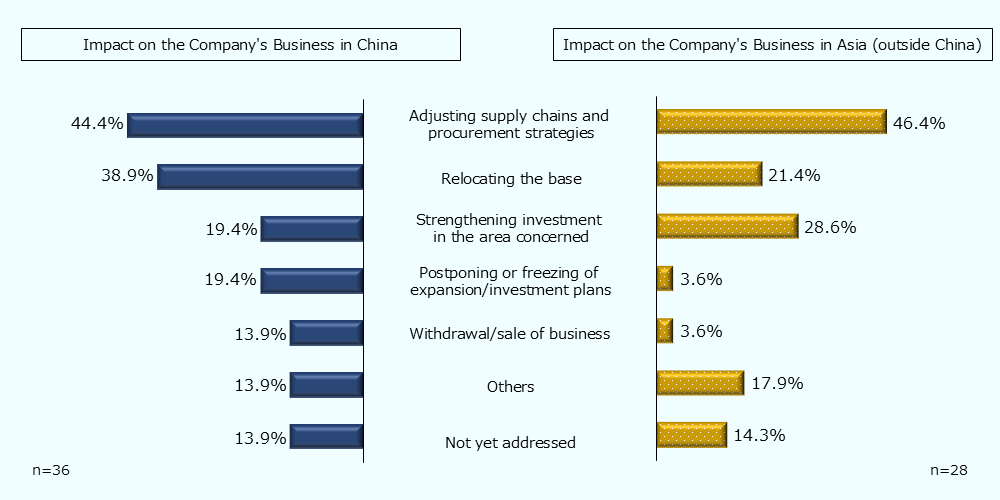
Supply chain and procurement strategies need to be adjusted both inside and outside China
Of the companies which responded "affected", just under half responded that they "had adjusted their supply chains and procurement strategies in the area concerned" as one of their countermeasures. In terms of specific measures, it showed a tendency to downsize its business in China, such as "changed its investment destination from China to other Asian regions" and "adjusted each production amount to direct production in China to only the Chinese market, and for other bases in Southeast Asia to take responsibility for production for other regions." On the other hand, there was a company that responded that they "are expanding investment in China targeting specific industries and markets."
-
Note1:
Multiple selections are allowed. Companies that selected at least one option were considered valid.
-
Note2:
This question was asked to companies that answered "significant" or "to some extent" to the question of whether the increasing geopolitical risks due to the U.S.-China conflict are affecting the business in China and other Asian countries.
-
Source:
JETRO's survey "Impact of Structural Changes in Global Value Chains (GVCs)"
Measures aimed at hedging risks against China are prominent
Chart 1-8: Specific measures of global companies' in light of the impact of the U.S.-China conflict.
| Countermeasures in China | Specific details |
|---|---|
| Adjusting supply chains and procurement strategies |
|
| Relocating the base |
|
| Strengthening investment in the area concerned |
|
| Postponing or freezing of expansion/ investment plans |
|
| Withdrawal/sale of business |
|
| Not yet addressed |
|
| Countermeasures in other Asian countries | Specific details |
|---|---|
| Adjusting supply chains and procurement strategies |
|
| Strengthening investment in the area concerned |
|
| Relocating the base |
|
| Others |
|
| Not yet addressed |
|
-
Source:
JETRO's survey "Impact of Structural Changes in Global Value Chains (GVCs)"
JETRO Invest Japan Report 2024
-
Section1.
-
Section2.
-
Section3.
-
Section1.
-
Section2.
-
Section3.
-
Section4.
-
[Column]
-
[Column]
-
Section5.
-
[Column]
-
Section6.
-
[Column]
-
Section1.
-
Section2.
-
Section3.
-
Section4.
Laws and Regulations on Setting Up Business in Japan Pamphlet

The pamphlet "Laws & Regulations" is available in PDF, and outlines basic information about laws, regulations and procedures related to setting up a business in Japan. It is available in 8 languages (Japanese, English, German, French, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Korean and Vietnamese).
You can download via the "Request Form" button below.
Contact Us
Investing in and collaborating with Japan
We will do our very best to support your business expansion into and within Japan as well as business collaboration with Japanese companies. Please feel free to contact us via the form below for any inquiries.
Inquiry FormJETRO Worldwide
Our network covers over 50 countries worldwide. You can contact us at one of our local offices near you for consultation.
Worldwide Offices