JETRO Invest Japan Report 2018 (Summary)3. Trend in Inward FDI in Japan
– Foreign Investment Contributing to the Emergence of Innovation
Foreign investment bringing innovation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution field to Japan and in turn creating new value
(1) “Connecting” with IoT to make normally hidden info “visible”
- Siemens (Germany): Contributes to productivity improvements and equipment failure predictions at plants by making work time and operational information “visible”
- Philips (Netherlands): Offers healthcare solutions which utilize data obtained from devices such as medical treatment equipment
- NextDrive (Taiwan): Provides smart energy management solutions by helping to make household energy usage “visible”
(2) FinTech bringing change to Japanese financial services
- QR code payment services:Alibaba (China) , Tencent (China)
- Cashless payment services using the latest technologies such as biometrics: Coolpay (Singapore)
- A system that effectively detects insurance claims that look fraudulently suspicious by using AI:Shift Technology (France)
- Overseas money transfer services:TransferWise (UK) , WorldRemit (UK) , Flywire (US)
(3) Foreign-affiliated companies working with existing companies to produce sharing services unique to Japan
- Vacation rental sites:Airbnb (US) , HomeAway (US) , Tujia (China) , Zizaike (China) , Keycafe (Canada)
- Ride-share:Uber Technologies (US) , Didi Chuxing (China) , Taiwan Taxi (Taiwan) , Via (US)
- Share bicycles and scooter:Mobike (China) , Gogoro (Taiwan)
(4) Technologies of foreign-affiliated companies adopted by industries predominately developed in Japan
- Beckhoff Automation (Germany): Toyota Motor Corporation has adopted the open industrial network protocol developed by Beckhoff as a standard field network for IoT in plants.
- Mermec (Italy): A trial introduction of a track diagnostic system developed by Mermec was decided for the track of the Sanyo Shinkansen Line of JR West.
Foreign-affiliated companies involved in the emergence of innovation in Japan via open innovation
(1) Aim to use and commercialize research seeds and address social issues
- J&J Innovation (US) with Osaka University
- Nihon L’Oréal (France) with the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS)
(2) Aim to use data to address social issues
- Philips Japan (Netherlands) with Tohoku University
- Philips Japan (Netherlands) with the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center (NCVC)
- GE Healthcare Japan (US) with the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center (NCVC)
(3) Make use of research seeds via the fostering of Japanese startups
- Bayer Yakuhin (Germany): Opened an incubation lab in Kobe with the aim of supporting startups in the bio field.
- Visa (US): Staged a startup competition program in Japan.
- Metlife (US): Held a program to assist startups in bringing to fruition inventive ideas in the field of health and wellness.
(4) Fuse together specialty fields on both sides to develop new products
- NTQ Solution (Vietnam): Developed a contactless computer security system that automatically logs on and logs off for users together with a Japanese company.
- Agilis Biotherapeutics (US): Established a joint venture with a Japanese company and opened an R&D center in Kawasaki, Kanagawa to develop new gene therapeutics.
Foreign-affiliated companies participating in the forming of Japanese startup ecosystem
Foreign affiliated companies are successively using their strengths – the abundant experience and successes achieved abroad – to make inroads into Japan.
(1) Startup Ecosystem in Japan (Focused on foreign-affiliated companies)
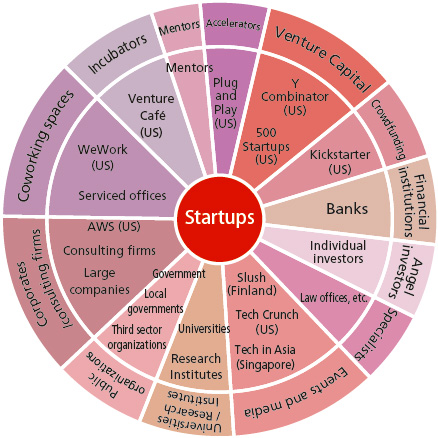
[Note] Classified by JETRO focusing on the representative factors of the foreign-affiliated companies introduced as examples in Chapter 3.
(2) Recent examples of ecosystem actors entering Japan
-
WeWork (US)
- A big US player in the coworking space field. Opened their first office in Japan in February 2018, and in half a year they have successively extended their presence to six offices.
- It has offices in almost 300 locations across the globe (as of June 2018), and connects more than 260,000 members on a global scale, stimulating each other and creating new businesses and innovation.
-
Plug and Play (US)
- One of the world’s biggest technology accelerators and venture capital providers, advanced into Shibuya, Tokyo in July 2017.
- They operate accelerator programs with top companies in Japan, cored around business axis of FinTech, and IoT.
- They offer various forms of mentoring and business know-hows needed to grow a startup through a three-months program.
- Looking to invest in 50 startups in Japan by 2020.
-
500 Startups (US)
- A venture capital company that works on fostering of entrepreneurs through investment to Japanese startups.
- Entered into a partnership with the City of Kobe in 2016, annually staging acceleration programs.
- There are some startups who have received venture capital and entered into partnerships with companies.
-
Venture Café (US)
- Opened “Venture Café Tokyo” in March 2018, offers networking events and seminars for startups.
- Entrepreneurs and investors can interact to expand their contacts and get opportunities to pick up business hints through the events.
- Works on activities co-partnered by government bodies and local governments such as “J-Startup”, a startup support program run under a partnership between the public and private sectors.
Foreign investment for creating innovation in local regions
(1) Fukuoka City: Aiming to be a “Startup City” through National Strategic Special Zone and partnerships with overseas
- Started Startup Visa under the National Strategic Special Zones system in 2015 for the first time in Japan.
- Established “Fukuoka Growth Next,” a startup support facility, supporting foreign startups’ activities in Fukuoka City.
- Develops close ties with 14 locales in 10 countries and regions (as of September 2018) promoting cooperation in enabling startups to mutually make inroads into each other’s countries/regions.
(2) Osaka City: On the frontline of international conference-led innovation and solutions for social challenges
- Supports entrepreneurs, establishing the “Osaka Innovation Hub” (OIH) as a place for supporting the creation of innovation.
- Held the international innovation conference “Hack Osaka 2018” inviting eight foreign startups to the pitch contest.
- “Hack Osaka 2019” has been selected as a project for Regional Business Conference (RBC).
(3) Kobe City: Teaming up with foreign-affiliates to offer entrepreneurs a platform for success
- Stages the acceleration program “500 Kobe Accelerator” in partnership with a global venture capital firm and accelerator, 500 Startups.
- Selected FlyData, a US startup involved in management support using big data and AI, with “Urban Innovation KOBE” which draws applicants from a wide range of startups working on solutions to regional administrative issues.
2018

-
1. Recent Situation of Inward FDI in Japan
 (1.7MB)
(1.7MB)
-
2. Toward Improvement of Business Environment
 (469KB)
(469KB)
-
3. Trend in Inward FDI in Japan – Foreign Investment Contributing to the Emergence of Innovation
 (1.6MB)
(1.6MB)
-
4. Perception of the Business Environment in Japan among Foreign-affiliated Companies
 (440KB)
(440KB)
-
5. JETRO Efforts to Promote Investment in Japan
 (3.5MB)
(3.5MB)
Contact Us
Investing in and collaborating with Japan
We will do our very best to support your business expansion into and within Japan as well as business collaboration with Japanese companies. Please feel free to contact us via the form below for any inquiries.
Inquiry FormJETRO Worldwide
Our network covers over 50 countries worldwide. You can contact us at one of our local offices near you for consultation.
Worldwide Offices