JETRO Invest Japan Report 2018 (Summary)2. Toward Improvement of Business Environment
Further improving the business environment and contributing to more inward FDI into Japan
(1) Establishment of project-based “Regulatory Sandbox” system
- A mechanism that creates an environment where innovative technologies and business models can be demonstrated without restrictions imposed by existing regulations, and that enables data collection that will lead to swift validation and regulatory reforms.
- Organized the GoJ’s Regulatory Sandbox Team and started preliminary consultations and acceptance of applications in June 2018.
Project-based “Regulatory Sandbox” system and its relationship to other systems for revising regulations
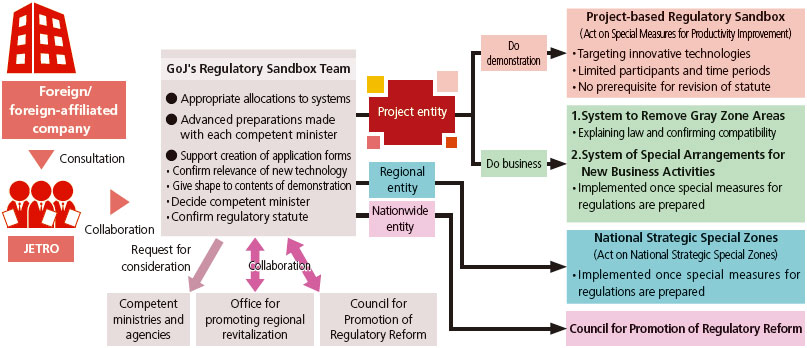
[Source] Innovative Technology/Businessmodel Evaluation Committee for Regulatory Sandbox in Japan
(2) Moves toward improvement of World Bank “Doing Business” ranking
- Realize completion of formalities within 24 hours during FY2019
- Use of IT in court proceedings, and introduction of web conferences for court cases
- Improvement of port logistics by reducing in freight holding time
apan’s overall ranking (2019) (out of 190 countries)(-: abbreviation)
| Rank | Country/region |
|---|---|
| 1 | New Zealand |
| 2 | Singapore |
| 3 | Denmark |
| 4 | Hong Kong |
| 5 | Korea, Rep |
| 6 | Georgia |
| 7 | Norway |
| 8 | US |
| 9-31 | - |
| Rank | Country/region |
|---|---|
| 32 | France |
| 33 | Poland |
| 34 | Portugal |
| 35 | Czech Republic |
| 36 | Netherlands |
| 37 | Belarus |
| 38 | Switzerland |
| 39 | Japan |
Details of the Japan's overall ranking

[Notes] Numbers indicate the rankings out of 190 countries.
[Source] "Doing Business 2019" (World Bank)
(3) 20% reduction in cost for administrative procedures
- The basic implementing plans (simplification plans) formulated by ministries and agencies have been examined and revised.
- The cost reduction benefit in targeted fields is expected to be 73.15 million hours (186 billion yen, a 22.3% reduction).
Prospect of administrative procedure costs and number of hours reduced by area
| Area | Target cases/procedures for basic plan formulation Total Number of Cases Processed (Number of Procedures Processed) | Target cases/procedures for cost measurement Total Number of Cases Processed (Number of Procedures Processed) | Number of Hours Spent (Equivalent Monetary Value) | Per Case | Number of Hours Reduced (Equivalent Monetary Value) | Per Case | Reduction Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Licensing |
6,519,196 cases (786 procedures) |
5,253,226 cases (330 procedures) |
141.73 million hours (360.4 billion yen) |
27.0 hours |
29.6 million hours (75.3 billion yen) |
5.6 hours |
20.9% |
| Social Insurance |
62,716,706 cases (105 procedures) |
56,806,812 cases (28 procedures) |
122.11 million hours (310.5 billion yen) |
2.1 hours |
29.22million hours (74.3 billion yen) |
0.5 hours |
23.9% |
| Surveys and Statistics |
7,169,681 cases (153 procedures) |
6,811,452 cases (98 procedures) |
23.93 million hours (60.9 billion yen) |
3.5 hours |
5.62 million hours (14.3 billion yen) |
0.8 hours |
23.5% |
| Labor Management |
3,304,726 cases (71 procedures) |
3,013,296 cases (15 procedures) |
15.14 million hours (38.5 billion yen) |
5.0 hours |
3.06 million hours (7.8 billion yen) |
1.0 hours |
20.2% |
| Subsidies |
297,660 cases (74 procedures) |
292,598 cases (56 procedures) |
11 million hours (28 billion yen) |
37.6 hours |
2.3 million hours (5.8 billion yen) |
7.9 hours |
20.9% |
| Commercial Registration |
998,850 cases (33 procedures) |
595,272 cases (2 procedures) |
8.53 million hours (21.7billion yen) |
14.3 hours |
1.71 million hours (4.3 billion yen) |
2.9 hours |
20.0% |
| Certificate of Employment |
2.46 million cases (1 procedure) |
2.46 million cases (1 procedure) |
5.56 million hours (14.1billion yen) |
2.3 hours |
1.64 million hours (4.2 billion yen) |
0.7 hours |
30.0% |
| Total |
83,466,819 cases (1,223procedures) |
75,232,656 cases (530procedures) |
328 million hours (834.1 billion yen) |
4.4 hours |
73.15 million hours (186 billion yen) |
1.0 hours |
22.3% |
(4) Inviting more foreign professionals into Japan
- Inviting more foreign entrepreneurs – extending period of stay to maximum of one year for preparation of starting a business
- Establishment of new status of residence for working in Japan
- "Business Manager" status of residence acquisition for coworking space now feasible
(5) Initiatives toward expanding Japan's inward FDI into regional areas
- Support Program for Regional Foreign Direct Investment in Japan
- Regional Business Conference
Image of Support Program for Regional Foreign Direct Investment in Japan

[Source] Council for Promotion of Foreign Direct Investment in Japan (6th meeting)
(6) Tax reform
- Establishing a tax system pertaining to the promotion of information collaboration investment (Connected Industries Tax System)
- Establishing a measure for smooth business restructuring via stock acquisition by way of compensation through ownership of company stock
Image of a measure for smooth business restructuring via stock acquisition by way of compensation through ownership of company stock
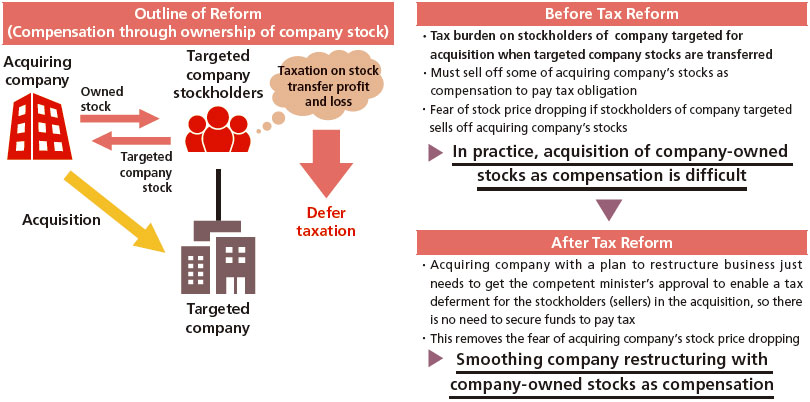
[Source] FY2018 Tax Reform pertaining to Economy, Trade and Industry (Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry)
(7) Enhancement of corporate governance
- Revision of corporate governance code(Jun 1, 2018)
Business environmental improvement efforts till now
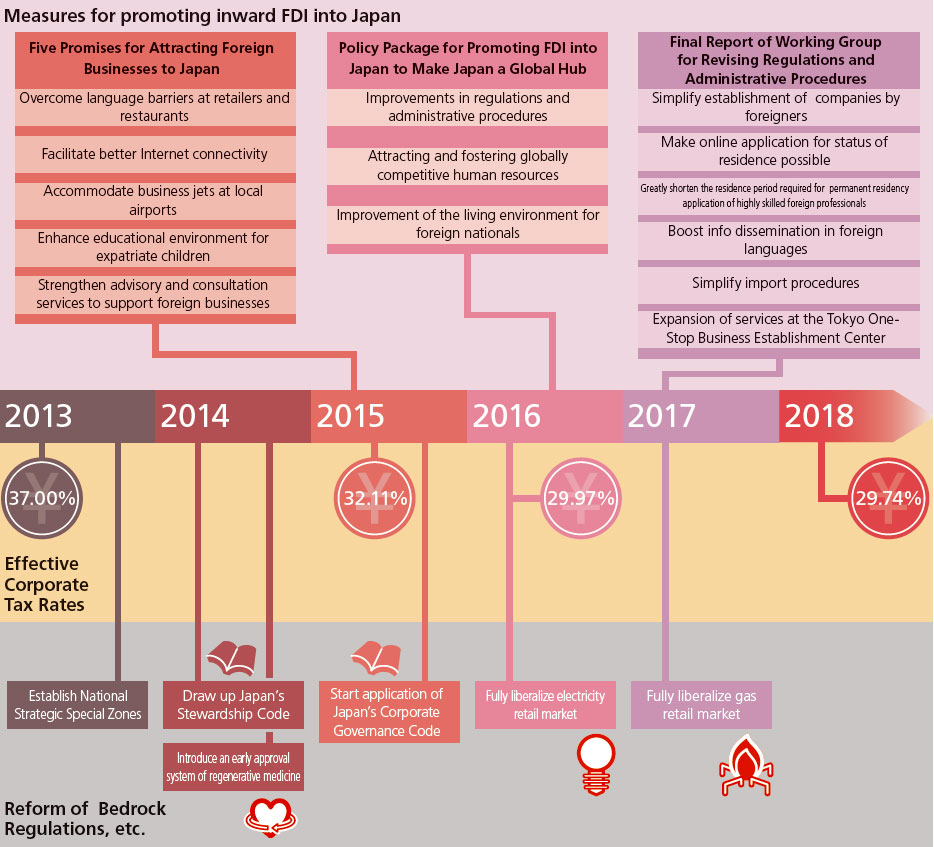
Description
This chart illustrates the efforts taken by the government to improve the business environment from 2013 to 2018 in chronological order in three categories: "measures for promoting inward FDI into Japan," "effective corporate tax rates" and "reform of bedrock regulations, etc."
The following measures for promoting inward FDI into Japan are included:
- "Five Promises for Attracting Foreign Businesses to Japan" (1. Overcoming language barriers at retailers and restaurants, 2. Facilitating better internet connectivity, 3. Accommodating business jets at local airports, 4. Enhancing the educational environment for expatriate children, 5. Strengthening advisory and consultation services to support foreign businesses) announced in 2015
- The "Policy Package for Promoting FDI into Japan to Make Japan a Global Hub" (1. Improvements in regulations and administrative procedures, 2. Attracting and fostering globally competitive human resources, 3. Improvement of the living environment for foreign nationals) announced in 2016
- The "Final Report of Working Group for Revising regulations and Administrative Procedures" (1. Simplifying establishment of companies by foreigners, 2. Making online application for status of residence possible, 3. Greatly shortening the residence period required to apply for permanent residency by highly skilled foreign professionals, 4. Boosting information dissemination in foreign languages, 5. Simplifying import procedures, 6. Expansion of services at the Tokyo One-Stop Business Establishment Center) announced in 2017
The effective corporate tax rate has been lowered to 37.00% in 2013, 32.11% in 2015, 29.97% in 2016, and 29.74% in 2018.
On the topic of reform of bedrock regulations, the following are mentioned:
- Establishment of National Strategic Special Zones in 2013
- Drawing up Japan's Stewardship Code and introduction of an early approval system for regenerative medicine in 2014
- Application of Japan's Corporate Governance Code in 2015
- Full liberalization of electricity market in 2016
- Full liberalization of gas retail market in 2018
2018

-
1. Recent Situation of Inward FDI in Japan
 (1.7MB)
(1.7MB)
-
2. Toward Improvement of Business Environment
 (469KB)
(469KB)
-
3. Trend in Inward FDI in Japan – Foreign Investment Contributing to the Emergence of Innovation
 (1.6MB)
(1.6MB)
-
4. Perception of the Business Environment in Japan among Foreign-affiliated Companies
 (440KB)
(440KB)
-
5. JETRO Efforts to Promote Investment in Japan
 (3.5MB)
(3.5MB)
Contact Us
Investing in and collaborating with Japan
We will do our very best to support your business expansion into and within Japan as well as business collaboration with Japanese companies. Please feel free to contact us via the form below for any inquiries.
Inquiry FormJETRO Worldwide
Our network covers over 50 countries worldwide. You can contact us at one of our local offices near you for consultation.
Worldwide Offices