JETRO Global Connection -Accelerate Innovation with Japan-
Report
Even Covid-19 Can't Stop Them! Taking Up a New Challenge with a Canadian AI based Hand Tracking and Gesture Recognition Start-up
-The rising importance of open innovation by Japan’s SMEsand start-ups-
(JAPAN)
September 7, 2020

Open innovation approaches in Japan are not confined to major companies. Today, when there are increasing opportunities for use of external resources, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and start-up firms capable of agile action may have the advantage in some cases. For Japan's SMEs and start-ups, open innovation is acquiring increasing importance as a means of overcoming the limitations of their own business resources.
Involved in the commercialization of image recognition technology, Sense Things Japan INC. concluded a partnership agreement with Motion Gestures (MG), a Canadian artificial intelligence (AI) start-up, in August 2020. MG is developing software for recognition of hand gestures using its AI-based hand tracking technology.
We asked Yutaka Umetsu, Director at Sense Things Japan, about the events leading up to collaboration with MG and the development of business going forward. (Interview date: August 26, 2020)
Events leading up to partnership with a Canadian start-up
The partnership goes back to the business talks we held with MG upon referral by JETRO at the CEATEC (see Note 1) show held in the autumn of 2019. At first, we discussed with MG with the intention as one of MG’s customers. MG was a fledgling start-up with about 10 employees, but MG’s software could recognize gestures with an accuracy of close to 100 percent, thanks to MG’s original algorithm developed. MG’s software was characterized by the lack of any need for the customers’ training data (see Note 2) at the time of application development; as long as there was a normal RGB camera, the application could recognize gestures in an instant. We checked the affinity with our own technology by means of the motion videos on cases of introduction provided on MG's movie website. While doing so, we held a series of web conferences and deepened our understanding of MG's technology.
Thereafter, we decided to exhibit the demonstration introducing MG's technology at the “Automotive World” show held in January 2020 at Tokyo Big Sight. We utilize the event as a stage of test marketing, and watched the reaction of people who came to the booth. As it turned out, interest ran high among the booth visitors, and some of them even made inquiries about a deal for the technology. For this reason, we decided in favor of the partnership. Nevertheless, we also faced a few difficulties in the beginning. Due to the Covid-19 pandemic, we were only able to have face-to-face meetings twice: once at the CEATEC venue and once in the week after the show. We pursued the negotiations for collaboration almost entirely online. We launched a project team within our company as well, appointed an engineer to be in charge, made repeated replications for verification, and gradually got things into shape as we worked toward the partnership agreement.

Detection of position coordinates for a total of 21 joints in real time
(photo provided by Sense Things Japan)
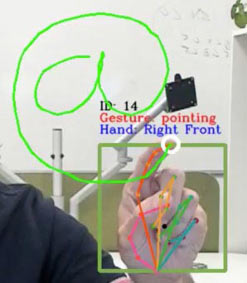
(photo provided by Sense Things Japan)
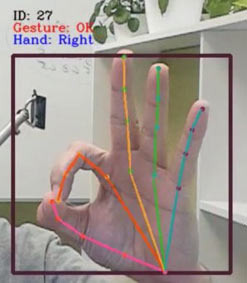
(photo provided by Sense Things Japan)
New needs brought about by the pandemic
Ideally, we would like to cultivate customers in Japan as well through shows and business talks abroad, but action to this end is limited by the effects of Covid-19. Nevertheless, we can promote MG's technology to customers even on an online basis, because the technology can be demonstrated with just a computer and a camera. MG wants to enter the market associated with the automotive industry, and is currently attempting approaches to a number of original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and Tier 1 companies in Japan. Viewed from the ergonomic perspective, when the drivers checked the monitors and operated switches the eyes were liable to be away from the front. In contrast, use of MG's technology makes it possible to operate switches with hand gestures, for safer driving. This technology has a wide scope of future applications, beginning with driver monitoring accompanying autonomous driving, for example. It is a non-contact technology of the sort which has become a focus of worldwide attention during the Covid-19 pandemic. We are identifying new needs in areas such as operation of buttons on elevators and vending machines using gestures, and applications on kiosk terminals and digital signage (see Note 3). We hope to broaden the business to encompass additional domains.
The issue is a shortage of talented human resources
Sense Things Japan has been actively engaged in open innovation with non-Japanese start-ups in the past as well. We have categorized the partnership with MG as one of our "overseas tech projects." Other projects may be exemplified by the partnership we formed in 2019 with the Israeli firm Silentium, which has the superiority in noise-canceling technology for use in vehicle cabins. The company’s technology reduces engine noise and road noise while driving. It has good prospects for applications not only in the automotive industry but also in fields such as headsets and air conditioning, where demand has expanded under the influence of the pandemic.
In connection with open innovation, we would like to continue unearthing start-ups in other countries, and are currently promoting several projects along this line. At the same time, an excessive number of projects translates into a shortage of talented human resources. The task is therefore the proper hiring and posting of personnel.
- Sense Things Japan
- Sense Things Japan is a Japanese company that positions imaging solutions as its core technology and develops mainly hardware products. The company is pursuing its own research and development of both hardware and software in the field of the Internet of Things (IoT), as well as related research and development consigned by other companies, and the manufacture and sale of diverse products. The company is headquartered in Tokyo and has a site for development and sales in Osaka. It employs 40 and was established in 2015.
- Motion Gestures
- Established in 2016, Motion Gestures is a Canadian start-up specializing in gesture recognition software based on machine learning. The company’s software performs AI-based hand tracking using position coordinates for finger joints.
(IOKI Tomoko)
Notes
1.
The Combined Exhibition of Advanced Technologies (CEATEC) is Japan's biggest trade show related to cyber-physical systems (CPS) and IoT technology. At CEATEC 2019, which was held in Makuhari Messe in 2019, JETRO set up the JETRO Global Connection exhibition, which had displays by 34 start-up firms from a total of 15 different countries and territories. JETRO also made arrangements for "meet-up" business talks with Japanese companies. It is planning to hold this exhibition online in 2020.
2.
Training data are data provided in advance in supervised machine learning. They correspond to correct answers.
3.
A collective term for media that disseminate information using displays and other electronic display devices.
-
US<>Japan VC Playbook: Bridging U.S. and Japanese Startup Ecosystems

February 2026
-
Overview of Japanese Startup Investment for US Venture Capitalists

May 2025
-
TBM, a Japanese Unicorn, is taking its environmentally conscious materials and solutions global

April 2025
-
Algal Bio’s Plan to Scale-up Microalgae Solutions for Food, Health, Climate, and more

March 2025
-
From Complexity to Clarity: How Veritus Helps Professors and Research Labs Innovate 5X Faster

February 2025
-
Biodata bank: Innovating Heat Risk Solutions for a Warming World

February 2025
-
Thermalytica’s Improved, Nano-scale Insulation Technology Could Change the World

January 2025
-
Techstars Tokyo Demo Day shows how Japan is Making Strides Towards Becoming a Global Startup Hub

December 2024



